우분투에 레디스를 설치하고 테스트하는 가장 쉬운 방법에 대해서 알아봅니다.

Table Of Contents
레디스 설치를 위한 준비
- redis 계정 생성 및 디렉토리 생성
- redis 계정에 sudo 권한 부여
- 패키지 목록 업데이트
#레디스 계정생성 및 디렉토리 생성
sudo useradd -d /home/redis redis
sudo passwd redis
sudo mkdir /home/redis
sudo chown redis:redis /home/redis
# redis 계정에 sudo 권한 부여
sudo addgroup redis sudo
'redis' 사용자를 'sudo' 그룹에 추가 중...
사용자 redis을(를) sudo 그룹에 등록 중
완료.
#패키지 목록 업데이트
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade
레디스 설치하기
레디스는 우분투에서는 apt-get으로 설치할 수 있습니다. 아래 명령어를 수행해서 레디스 설치와 설치후 서버가 정상적으로 떠있는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
# 레디스 설치
$ sudo apt-get install redis-server
# 레디스 설치 확인
$ redis-server --version
Redis server v=6.0.16 sha=00000000:0 malloc=jemalloc-5.2.1 bits=64 build=a3fdef44459b3ad6
#설치를 하면 다음과 같이 레디스 서버가 떠 있음
$ ps -ef |grep redis-server
redis 1200812 1 0 18:31 ? 00:00:02 /usr/bin/redis-server 127.0.0.1:6379
redis 1201511 1178115 0 18:58 pts/1 00:00:00 grep redis-server
레디스 설정파일
레디스 설정파일은 /etc/redis/redis.conf에 있습니다.
sudo vi /etc/redis/redis.conf
위의 명령어로 열어보면 memory management 섹션에 최대 메모리 허용량인 maxmemory와 memory-policy 정책이 있습니다. memory-policy 정책은 메모리 한계가 왔을때, 어떤 알고리즘으로 교체 정책을 실행하는가 입니다.
기본으로는 noeviction으로 교체하지 않고 내리지 않는 정책입니다.
############################## MEMORY MANAGEMENT ################################
# Set a memory usage limit to the specified amount of bytes.
# When the memory limit is reached Redis will try to remove keys
# according to the eviction policy selected (see maxmemory-policy).
#
# If Redis can't remove keys according to the policy, or if the policy is
# set to 'noeviction', Redis will start to reply with errors to commands
# that would use more memory, like SET, LPUSH, and so on, and will continue
# to reply to read-only commands like GET.
#
# This option is usually useful when using Redis as an LRU or LFU cache, or to
# set a hard memory limit for an instance (using the 'noeviction' policy).
#
# WARNING: If you have replicas attached to an instance with maxmemory on,
# the size of the output buffers needed to feed the replicas are subtracted
# from the used memory count, so that network problems / resyncs will
# not trigger a loop where keys are evicted, and in turn the output
# buffer of replicas is full with DELs of keys evicted triggering the deletion
# of more keys, and so forth until the database is completely emptied.
#
# In short... if you have replicas attached it is suggested that you set a lower
# limit for maxmemory so that there is some free RAM on the system for replica
# output buffers (but this is not needed if the policy is 'noeviction').
#
# maxmemory <bytes>
# MAXMEMORY POLICY: how Redis will select what to remove when maxmemory
# is reached. You can select one from the following behaviors:
#
# volatile-lru -> Evict using approximated LRU, only keys with an expire set.
# allkeys-lru -> Evict any key using approximated LRU.
# volatile-lfu -> Evict using approximated LFU, only keys with an expire set.
# allkeys-lfu -> Evict any key using approximated LFU.
# volatile-random -> Remove a random key having an expire set.
# allkeys-random -> Remove a random key, any key.
# volatile-ttl -> Remove the key with the nearest expire time (minor TTL)
# noeviction -> Don't evict anything, just return an error on write operations.
#
# LRU means Least Recently Used
# LFU means Least Frequently Used
#
# Both LRU, LFU and volatile-ttl are implemented using approximated
# randomized algorithms.
#
# Note: with any of the above policies, Redis will return an error on write
# operations, when there are no suitable keys for eviction.
#
# At the date of writing these commands are: set setnx setex append
# incr decr rpush lpush rpushx lpushx linsert lset rpoplpush sadd
# sinter sinterstore sunion sunionstore sdiff sdiffstore zadd zincrby
# zunionstore zinterstore hset hsetnx hmset hincrby incrby decrby
# getset mset msetnx exec sort
#
# The default is:
#
# maxmemory-policy noeviction
# LRU, LFU and minimal TTL algorithms are not precise algorithms but approximated
# algorithms (in order to save memory), so you can tune it for speed or
# accuracy. By default Redis will check five keys and pick the one that was
# used least recently, you can change the sample size using the following
예를들어 최대 사용 메모리양은 1G로 설정하고 1G를 초과할 시 메모리에 상주시키는 데이터는 가장 오래된 데이터를 지우고 가장 최근에 저장된 데이터를 사용하는 알고리즘은 LRU를 사용하는 경우 다음과 같이 지정할 수 있습니다.
maxmemory 1g
maxmemory-policy allkeys-lru
이렇게 설정을 바꾼 후에는 설정이 적용되도록 Redis를 재시작해야합니다.
$ sudo systemctl restart redis-server.service
레디스 테스트
레디스를 테스트하는 가장 간단한 방법은 레디스 CLI를 사용하는 것입니다.
레디스 CLI 실행
레디스 cli는 아래의 명령어로 실행 가능합니다.
$ redis-cli
127.0.0.1:6379> set key value [EX seconds|PX milliseconds|KEEPTTL] [NX|XX]
데이터 입력하기
가장 간단한 데이터 입력은 set 명령으로 가능합니다. set을 치면 그 뒤에 넣을 수 있는 명령 옵션들이 흐리게 보입니다.
set [key1] [value1]
127.0.0.1:6379> set key value [EX seconds|PX milliseconds|KEEPTTL] [NX|XX]

다음과 같이 간단하게 1의 key를 갖는 test 데이터를 입력해 볼 수 있습니다.
127.0.0.1:6379> set 1 "test"
OK
키 확인
키를 확인할 때에는 keys 명령어 뒤에 pattern을 넣어서 검색할 수 있습니다.
127.0.0.1:6379> keys pattern
전체 키를 확인하기 위해서 모든 패턴을 의미하는 "*"을 넣으면 아래와 같이 실행됩니다.
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
1) "1"
127.0.0.1:6379>
Value 가져오기
value를 가져올 때에는 get 명령으로 수행하며 key를 조건으로 입력합니다. get 명령어 뒤에는 반드시 key가 필요합니다.
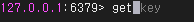
get [key]
127.0.0.1:6379> keys 1
1) "1"
127.0.0.1:6379> keys "test"
(empty array)
127.0.0.1:6379> get 1
"test"
127.0.0.1:6379>
전체 키 삭제
전체 키를 삭제하려면 flushall을 수행하면 됩니다.
flushall
127.0.0.1:6379> flushall
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
(empty array)
'DBMS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 그린플럼(Greenplum Database)와 고객(Customer) 리스트 (0) | 2023.12.07 |
|---|---|
| Greenplum mpp dbms의 github 알아보기 - source code layout (0) | 2023.12.06 |
| Greenplum mpp dbms의 github 알아보기 - source code layout (0) | 2023.12.03 |
| MPP DBMS Greenplum java jdbc 테스트 (0) | 2023.12.02 |
| MPP DBMS Greenplum 컴파일 후 데모 클러스터와 psql 테스트 (0) | 2023.12.02 |










